How to recover deleted files from PC?
Quick and easily recover your deleted files. Deleted a big file by accident? Missing files after a computer crash? No problem here; you can learn how to restore accidentally deleted personal files.
You know that you accidentally removed a file or deleted the contents of a file, and it is also frustrating if you have been working on something for days, weeks, or even months. Fortunately, it is not the end of the world to delete a file. Indeed, the file is in the recycling bin in many cases and can be recovered quickly
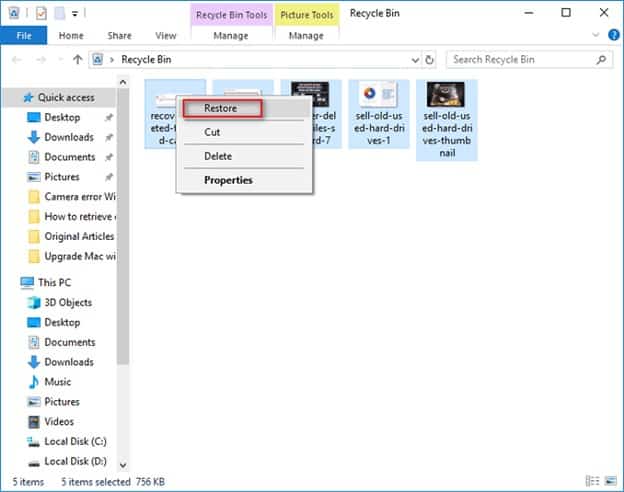
See the recycle bin.
Only double-click on the recycling bin or trashcan, and you will see all the inside. Have you noticed what you thought you were deleting? Just drag it back to your screen, and you’re nice to get there. If it isn’t in your trashcan, you can try to recover a deleted file in various other items.
I hope you’ve done backups. If that is the case, you can recover a previous version of the file through the backup service. Maybe it’s an old day, but one day better than losing it all.
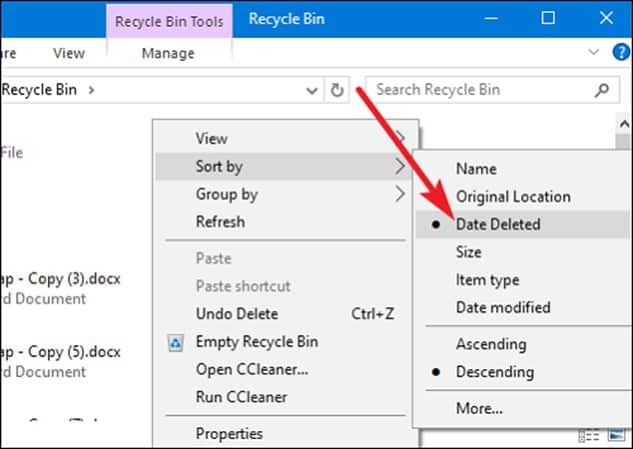
How to restore deleted files using the history of files?
I hope you have turned on file history backup if you don’t make any backups.
Choose Settings > Upgrading & Security > Backup > Attaching a drive if you are running Windows 10, select a hard drive or network location for backups.
To restore the missing document:
- Enter deleted files and select restore files using history files in the taskbar search box.
- Search for the file. You need to see all its versions, then use the arrows.
- Choose to restore to save the version in its current place when you find the version you want to. Press and hold (or right-click), select restore to, and then select a new location to save in another place.
No backups –Best option to recover deleted files.
The deleted file recovery program is a software to reload missing files from any storage medium. Files that have been deleted or lost by accident due to virus attack, breakdown of the hard drive, or otherwise can be recovered.
This software searches and find missing files for the storage medium. It can recover various file types, such as audio, video, contacts, e-mails, etc.
So, if you do not have any backups and your file is not in the trash. You may want to try one of many file recovery software’s out there.
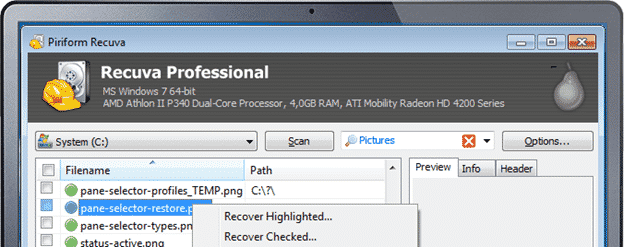
- Recuva: You can restore or re-delete the file by Recuva. It is possible to restore from the corrupted or formatted disc. It comes with a quick start assistant. It runs windows operating systems and supports 37 languages and more. You can find photos, songs, documents, videos, e-mails, etc. It can perform PC device, recycle bin, SD card, or MP3 player file recovery.
- Stellar Data Recovery: For customers and companies, Stellar Data Recovery is best. You could use a desktop, PC, tablet, cloud, disc, memory card, etc. It has restored software for files, photo recovery software, and software for smartphone recovery.
- Disk Drill, a Mac recovery tool now available on Windows, is another alternative. It supports file failure, rebooted hard drives, failed boot-ups, accidental deletions, and much more.
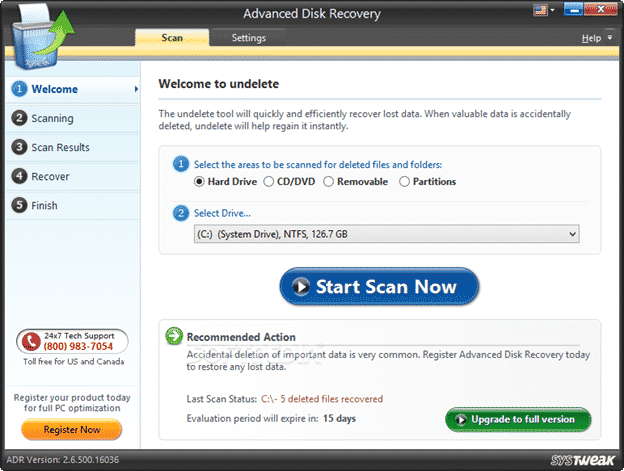
- Advanced Disk Recovery can restore missing or deleted files quickly. You may recover lost or deleted images from storage devices, USB devices, or SD cards, like images, audio, documents, etc.
The system is 100% secure and hassle-free. Without overwriting the original data, it will restore all lost information. This solution is available to many devices, including PC, tablet, SSD, USB, and Hard Disk.
Another opportunity to take into account: have you sent an e-mail to somebody? Have you saved a copy to a DropBox, iCloud, or SkyDrive cloud-based service? If so, then you should pick up a copy of it. Again, it’s better than nothing, even though you lose the new updates.
However, after knowing that you have accidentally deleted a picture, text, chart, report, or another file, you are approaching it, even so. And get the backups running, too, so you will have more options next time you’ll try to find a deleted file.
Conclusion
Data Recovery is not permanent, neither is it guaranteed. If it happens that you have deleted files or formatted a device ie hard drive, flash, it’s best advisable that you don’t continue using the device until the files have been recovered. This is because any new data saved will overwrite the deleted data rendering it unrecoverable. This means that, the files may be recovered but corrupt in unreadable format.
If unsuccessful in recovering the data, consult a data recovery company and get your files back. In some cases, deleted or formatted device may require specialized skills for successful recovery.